linkedin-skill-assessments
Python (Programming Language)
Q1. What is an abstract class?
- An abstract class is the name for any class from which you can instantiate an object.
- Abstract classes must be redefined any time an object is instantiated from them.
- Abstract classes must inherit from concrete classes.
- An abstract class exists only so that other “concrete” classes can inherit from the abstract class.
Q2. What happens when you use the build-in function any() on a list?
- The
any()function will randomly return any item from the list. - The
any()function returns True if any item in the list evaluates to True. Otherwise, it returns False. - The
any()function takes as arguments the list to check inside, and the item to check for. If “any” of the items in the list match the item to check for, the function returns True. - The
any()function returns a Boolean value that answers the question “Are there any items in this list?”
example
if any([True, False, False, False]) == True:
print('Yes, there is True')
>>> 'Yes, there is True'
Q3. What data structure does a binary tree degenerate to if it isn’t balanced properly?
- linked list
- queue
- set
- OrderedDict
Q4. What statement about static methods is true?
- Static methods are called static because they always return
None. - Static methods can be bound to either a class or an instance of a class.
- Static methods serve mostly as utility methods or helper methods, since they can’t access or modify a class’s state.
- Static methods can access and modify the state of a class or an instance of a class.
Q5. What are attributes?
- Attributes are long-form version of an
if/elsestatement, used when testing for equality between objects. - Attributes are a way to hold data or describe a state for a class or an instance of a class.
- Attributes are strings that describe characteristics of a class.
- Function arguments are called “attributes” in the context of class methods and instance methods.
Explanation Attributes defined under the class, arguments goes under the functions. arguments usually refer as parameter, whereas attributes are the constructor of the class or an instance of a class.
Q6. What is the term to describe this code?
count, fruit, price = (2, 'apple', 3.5)
tuple assignmenttuple unpackingtuple matchingtuple duplication
Q7. What built-in list method would you use to remove items from a list?
.delete()methodpop(my_list)del(my_list).pop()method
example
my_list = [1,2,3]
my_list.pop(0)
my_list
>>>[2,3]
Q8. What is one of the most common use of Python’s sys library?
- to capture command-line arguments given at a file’s runtime
- to connect various systems, such as connecting a web front end, an API service, a database, and a mobile app
- to take a snapshot of all the packages and libraries in your virtual environment
- to scan the health of your Python ecosystem while inside a virtual environment
Q9. What is the runtime of accessing a value in a dictionary by using its key?
- O(n), also called linear time.
- O(log n), also called logarithmic time.
- O(n^2), also called quadratic time.
- O(1), also called constant time.
Q10. What is the correct syntax for defining a class called Game, if it inherits from a parent class called LogicGame?
class Game(LogicGame): passdef Game(LogicGame): passdef Game.LogicGame(): passclass Game.LogicGame(): pass
Explanation: The parent class which is inherited is passed as an argument to the child class. Therefore, here the first option is the right answer.
Q11. What is the correct way to write a doctest?
- A
def sum(a, b):
"""
sum(4, 3)
7
sum(-4, 5)
1
"""
return a + b
- B
def sum(a, b):
"""
>>> sum(4, 3)
7
>>> sum(-4, 5)
1
"""
return a + b
- C
def sum(a, b):
"""
# >>> sum(4, 3)
# 7
# >>> sum(-4, 5)
# 1
"""
return a + b
- D
def sum(a, b):
###
>>> sum(4, 3)
7
>>> sum(-4, 5)
1
###
return a + b
Explanation - use ''' to start the doc and add output of the cell after >>>
Q12. What built-in Python data type is commonly used to represent a stack?
setlistNonedictionaryYou can only build a stack from scratch.
Q13. What would this expression return?
college_years = ['Freshman', 'Sophomore', 'Junior', 'Senior']
return list(enumerate(college_years, 2019))
[('Freshman', 2019), ('Sophomore', 2020), ('Junior', 2021), ('Senior', 2022)][(2019, 2020, 2021, 2022), ('Freshman', 'Sophomore', 'Junior', 'Senior')][('Freshman', 'Sophomore', 'Junior', 'Senior'), (2019, 2020, 2021, 2022)][(2019, 'Freshman'), (2020, 'Sophomore'), (2021, 'Junior'), (2022, 'Senior')]
Q14. What is the purpose of the “self” keyword when defining or calling instance methods?
selfmeans that no other arguments are required to be passed into the method.- There is no real purpose for the
selfmethod; it’s just historic computer science jargon that Python keeps to stay consistent with other programming languages. selfrefers to the instance whose method was called.selfrefers to the class that was inherited from to create the object usingself.
Simple example
class my_secrets:
def __init__(self, password):
self.password = password
pass
instance = my_secrets('1234')
instance.password
>>>'1234'
Q15. Which of these is NOT a characteristic of namedtuples?
- You can assign a name to each of the
namedtuplemembers and refer to them that way, similarly to how you would access keys indictionary. - Each member of a namedtuple object can be indexed to directly, just like in a regular
tuple. namedtuplesare just as memory efficient as regulartuples.- No import is needed to use
namedtuplesbecause they are available in the standard library.
We need to import it using:from collections import namedtuple
Q16. What is an instance method?
- Instance methods can modify the state of an instance or the state of its parent class.
- Instance methods hold data related to the instance.
- An instance method is any class method that doesn’t take any arguments.
- An instance method is a regular function that belongs to a class, but it must return
None.
Q17. Which statement does NOT describe the object-oriented programming concept of encapsulation?
- It protects the data from outside interference.
- A parent class is encapsulated and no data from the parent class passes on to the child class.
- It keeps data and the methods that can manipulate that data in one place.
- It only allows the data to be changed by methods.
Q18. What is the purpose of an if/else statement?
- It tells the computer which chunk of code to run if the instructions you coded are incorrect.
- It runs one chunk of code if all the imports were successful, and another chunk of code if the imports were not successful.
- It executes one chunk of code if a condition is true, but a different chunk of code if the condition is false.
- It tells the computer which chunk of code to run if the is enough memory to handle it, and which chunk of code to run if there is not enough memory to handle it.
Q19. What built-in Python data type is best suited for implementing a queue?
- dictionary
- set
- None. You can only build a queue from scratch.
- list
Q20. What is the correct syntax for instantiating a new object of the type Game?
my_game = class.Game()my_game = class(Game)my_game = Game()my_game = Game.create()
Q21. What does the built-in map() function do?
- It creates a path from multiple values in an iterable to a single value.
- It applies a function to each item in an iterable and returns the value of that function.
- It converts a complex value type into simpler value types.
- It creates a mapping between two different elements of different iterables.
Explanation: - The synax for map() function is list(map(function,iterable)). The simple area finder using map would be like this
import math
radius = [1,2,3]
area = list(map(lambda x: round(math.pi*(x**2), 2), radius))
area
>>> [3.14, 12.57, 28.27]
Q22. If you don’t explicitly return a value from a function, what happens?
- The function will return a RuntimeError if you don’t return a value.
- If the return keyword is absent, the function will return
None. - If the return keyword is absent, the function will return
True. - The function will enter an infinite loop because it won’t know when to stop executing its code.
Q23. What is the purpose of the pass statement in Python?
- It is used to skip the
yieldstatement of a generator and return a value of None. - It is a null operation used mainly as a placeholder in functions, classes, etc.
- It is used to pass control from one statement block to another.
- It is used to skip the rest of a
whileorfor loopand return to the start of the loop.
Q24. What is the term used to describe items that may be passed into a function?
- arguments
- paradigms
- attributes
- decorators
Q25. Which collection type is used to associate values with unique keys?
slotdictionaryqueuesorted list
Q26. When does a for loop stop iterating?
- when it encounters an infinite loop
- when it encounters an if/else statement that contains a break keyword
- when it has assessed each item in the iterable it is working on or a break keyword is encountered
- when the runtime for the loop exceeds O(n^2)
Q27. Assuming the node is in a singly linked list, what is the runtime complexity of searching for a specific node within a singly linked list?
- The runtime is O(n) because in the worst case, the node you are searching for is the last node, and every node in the linked list must be visited.
- The runtime is O(nk), with n representing the number of nodes and k representing the amount of time it takes to access each node in memory.
- The runtime cannot be determined unless you know how many nodes are in the singly linked list.
- The runtime is O(1) because you can index directly to a node in a singly linked list.
Q28. Given the following three list, how would you create a new list that matches the desired output printed below?
fruits = ['Apples', 'Oranges', 'Bananas']
quantities = [5, 3, 4]
prices = [1.50, 2.25, 0.89]
#Desired output
[('Apples', 5, 1.50),
('Oranges', 3, 2.25),
('Bananas', 4, 0.89)]
- A
output = []
fruit_tuple_0 = (first[0], quantities[0], price[0])
output.append(fruit_tuple)
fruit_tuple_1 = (first[1], quantities[1], price[1])
output.append(fruit_tuple)
fruit_tuple_2 = (first[2], quantities[2], price[2])
output.append(fruit_tuple)
return output
- B
i = 0
output = []
for fruit in fruits:
temp_qty = quantities[i]
temp_price = prices[i]
output.append((fruit, temp_qty, temp_price))
i += 1
return output
- C
groceries = zip(fruits, quantities, prices)
return groceries
>>> [
('Apples', 5, 1.50),
('Oranges', 3, 2.25),
('Bananas', 4, 0.89)
]
- D
i = 0
output = []
for fruit in fruits:
for qty in quantities:
for price in prices:
output.append((fruit, qty, price))
i += 1
return output
Q29. What happens when you use the built-in function all() on a list?
- The
all()function returns a Boolean value that answers the question “Are all the items in this list the same? - The
all()function returns True if all the items in the list can be converted to strings. Otherwise, it returns False. - The
all()function will return all the values in the list. - The
all()function returns True if all items in the list evaluate to True. Otherwise, it returns False.
Explanation - all() returns true if all in the list are True, see example below
test = [True,False,False,False]
if all(test) is True:
print('Yeah all are True')
else:
print('There is an imposter')
>>> 'There is an imposter'
Q30. What is the correct syntax for calling an instance method on a class named Game?
(Answer format may vary. Game and roll (or dice_roll) should each be called with no parameters.)
- A
>>> dice = Game()
>>> dice.roll()
- B
>>> dice = Game(self)
>>> dice.roll(self)
- C
>>> dice = Game()
>>> dice.roll(self)
- D
>>> dice = Game(self)
>>> dice.roll()
Q31. What is the algorithmic paradigm of quick sort?
- backtracking
- dynamic programming
- decrease and conquer
- divide and conquer
Q32. What is runtime complexity of the list’s built-in .append() method?
- O(1), also called constant time
- O(log n), also called logarithmic time
- O(n^2), also called quadratic time
- O(n), also called linear time
Q33. What is key difference between a set and a list?
- A set is an ordered collection unique items. A list is an unordered collection of non-unique items.
- Elements can be retrieved from a list but they cannot be retrieved from a set.
- A set is an ordered collection of non-unique items. A list is an unordered collection of unique items.
- A set is an unordered collection unique items. A list is an ordered collection of non-unique items.
Q34. What is the definition of abstraction as applied to object-oriented Python?
- Abstraction means that a different style of code can be used, since many details are already known to the program behind the scenes.
- Abstraction means the implementation is hidden from the user, and only the relevant data or information is shown.
- Abstraction means that the data and the functionality of a class are combined into one entity.
- Abstraction means that a class can inherit from more than one parent class.
Q35. What does this function print?
def print_alpha_nums(abc_list, num_list):
for char in abc_list:
for num in num_list:
print(char, num)
return
print_alpha_nums(['a', 'b', 'c'], [1, 2, 3])
- A
a 1
a 2
a 3
b 1
b 2
b 3
c 1
c 2
c 3
- B
['a', 'b', 'c'], [1, 2, 3]
- C
aaa
bbb
ccc
111
222
333
- D
a 1 2 3
b 1 2 3
c 1 2 3
Q36. Pick correct representation of doctest for function in Python.
- :
def sum(a, b):
# a = 1
# b = 2
# sum(a, b) = 3
return a + b
- :
def sum(a, b):
"""
a = 1
b = 2
sum(a, b) = 3
"""
return a + b
- :
def sum(a, b):
"""
>>> a = 1
>>> b = 2
>>> sum(a, b)
3
"""
return a + b
- :
def sum(a, b):
'''
a = 1
b = 2
sum(a, b) = 3
'''
return a + b
Explanation: Use """ to start and end the docstring and use >>> to represent the output. If you write this correctly you can also run the doctest using build-in doctest module
Q37. Suppose a Game class inherits from two parent classes: BoardGame and LogicGame. Which statement is true about the methods of an object instantiated from the Game class?
- When instantiating an object, the object doesn’t inherit any of the parent class’s methods.
- When instantiating an object, the object will inherit the methods of whichever parent class has more methods.
- When instantiating an object, the programmer must specify which parent class to inherit methods from.
- An instance of the Game class will inherit whatever methods the BoardGame and LogicGame classes have.
Q38. What does calling namedtuple on a collection type return?
- a generic object class with iterable parameter fields
- a generic object class with non-iterable named fields
- a tuple subclass with non-iterable parameter fields
- a tuple subclass with iterable named fields
Example
# namedtuple function accepts the following arguments to generate a class
from collections import namedtuple
>>> Point = namedtuple('Point',['x','y'])
>>> point = Point(100, 200)
>>> point
Point(x=100, y=200)
# Which let you use both unpacking and iteration to access
>>> x, y = point
>>> print(f'({x}, {y})')
(100, 200)
>>> for coordinate in point:
print(coordinate)
100
200
Q39. What symbol(s) do you use to assess equality between two elements?
&&===||
Q40. Review the code below. What is the correct syntax for changing the price to 1.5?
fruit_info = {
'fruit': 'apple',
'count': 2,
'price': 3.5
}
fruit_info ['price'] = 1.5my_list [3.5] = 1.51.5 = fruit_info ['price]my_list['price'] == 1.5
Q41. What value would be returned by this check for equality?
5 != 6
yesFalseTrueNone
Explanation - != is equivalent to not equal to in python
Q42. What does a class’s __init__() method do?
- It makes classes aware of each other if more than one class is defined in a single code file.
- It is included to preserve backwards compatibility from Python 3 to Python 2, but no longer needs to be used in Python 3.
- It is a method that acts as a constructor and is called automatically whenever a new object is created from a class. It sets the initial state of a new object.
- It initializes any imports you may have included at the top of your file.
Example:
class test:
def __init__(self):
print('I came here without your permission lol')
pass
t1 = test()
>>> 'I came here without your permission lol'
Q43. What is meant by the phrase “space complexity”?
How many microprocessors it would take to run your code in less than one secondHow many lines of code are in your code fileThe amount of space taken up in memory as a function of the input sizeHow many copies of the code file could fit in 1 GB of memory
Q44. What is the correct syntax for creating a variable that is bound to a dictionary?
fruit_info = {'fruit': 'apple', 'count': 2, 'price': 3.5}fruit_info =('fruit': 'apple', 'count': 2,'price': 3.5 ).dict()fruit_info = ['fruit': 'apple', 'count': 2,'price': 3.5 ].dict()fruit_info = to_dict('fruit': 'apple', 'count': 2, 'price': 3.5)
Q45. What is the proper way to write a list comprehension that represents all the keys in this dictionary?
fruits = {'Apples': 5, 'Oranges': 3, 'Bananas': 4}
fruit_names = [x in fruits.keys() for x]fruit_names = for x in fruits.keys() *fruit_names = [x for x in fruits.keys()]fruit_names = x for x in fruits.keys()
Q46. What is the purpose of the self keyword when defining or calling methods on an instance of an object?
selfrefers to the class that was inherited from to create the object usingself.- There is no real purpose for the
selfmethod. It’s just legacy computer science jargon that Python keeps to stay consistent with other programming languages. selfmeans that no other arguments are required to be passed into the method.selfrefers to the instance whose method was called.
Explanation: - Try running the example of the Q42 without passing self argument inside the __init__, you’ll understand the reason. You’ll get the error like this __init__() takes 0 positional arguments but 1 was given, this means that something is going inside even if haven’t specified, which is instance itself.
Q47. What statement about the class methods is true?
- A class method is a regular function that belongs to a class, but it must return None.
- A class method can modify the state of the class, but they can’t directly modify the state of an instance that inherits from that class.
- A class method is similar to a regular function, but a class method doesn’t take any arguments.
- A class method hold all of the data for a particular class.
Q48. What does it mean for a function to have linear runtime?
- You did not use very many advanced computer programming concepts in your code.
- The difficulty level your code is written at is not that high.
- It will take your program less than half a second to run.
- The amount of time it takes the function to complete grows linearly as the input size increases.
Q49. What is the proper way to define a function?
def getMaxNum(list_of_nums): # body of function goes herefunc get_max_num(list_of_nums): # body of function goes herefunc getMaxNum(list_of_nums): # body of function goes heredef get_max_num(list_of_nums): # body of function goes here
Q50. According to the PEP 8 coding style guidelines, how should constant values be named in Python?
- in camel case without using underscores to separate words -- e.g.
maxValue = 255 - in lowercase with underscores to separate words -- e.g.
max_value = 255 - in all caps with underscores separating words -- e.g.
MAX_VALUE = 255 - in mixed case without using underscores to separate words -- e.g.
MaxValue = 255
Q51. Describe the functionality of a deque.
- A deque adds items to one side and remove items from the other side.
- A deque adds items to either or both sides, but only removes items from the top.
- A deque adds items at either or both ends, and remove items at either or both ends.
- A deque adds items only to the top, but remove from either or both sides.
Explanation - deque is used to create block chanin and in that there is first in first out approch, which means the last element to enter will be the first to leave.
Q52. What is the correct syntax for creating a variable that is bound to a set?
my_set = {0, 'apple', 3.5}my_set = to_set(0, 'apple', 3.5)my_set = (0, 'apple', 3.5).to_set()my_set = (0, 'apple', 3.5).set()
Q53. What is the correct syntax for defining an __init__() method that takes no parameters?
- :
class __init__(self):
pass
- :
def __init__():
pass
- :
class __init__():
pass
- :
def __init__(self):
pass
Q54. Which of the following is TRUE About how numeric data would be organised in a Binary Search Tree?
- For any given node in a binary search tree, the value of the node is greater than all the values in the node’s left subtree and less than the ones in its right subtree.
- Binary Search Tree cannot be used to organize and search through numeric data, given the complication that arise with very deep trees.
- The top node of the binary search tree would be an arbitrary number. All the nodes to the left of the top node need to be less than the top node’s number, but they don’t need to ordered in any particular way.
- The smallest numeric value would go in the top most node. The next highest number would go in its left child node, the the next highest number after that would go in its right child node. This pattern would continue until all numeric values were in their own node.
Q55. Why would you use a decorator?
- A decorator is similar to a class and should be used if you are doing functional programming instead of object oriented programming.
- A decorator is a visual indicator to someone reading your code that a portion of your code is critical and should not be changed.
- You use the decorator to alter the functionality of a function without having to modify the functions code.
- An import statement is preceded by a decorator, python knows to import the most recent version of whatever package or library is being imported.
Q56. When would you use a for loop?
- Only in some situations, as loops are used only for certain type of programming.
- When you need to check every element in an iterable of known length.
- When you want to minimize the use of strings in your code.
- When you want to run code in one file for a function in another file.
Q57. What is the most self-descriptive way to define a function that calculates sales tax on a purchase?
- :
def tax(my_float):
'''Calculates the sales tax of a purchase. Takes in a float representing the subtotal as an argument and returns a float representing the sales tax.'''
pass
- :
def tx(amt):
'''Gets the tax on an amount.'''
- :
def sales_tax(amount):
'''Calculates the sales tax of a purchase. Takes in a float representing the subtotal as an argument and returns a float representing the sales tax.'''
- :
def calculate_sales_tax(subtotal):
pass
Q58. What would happen if you did not alter the state of the element that an algorithm is operating on recursively?
- You do not have to alter the state of the element the algorithm is recursing on.
- You would eventually get a KeyError when the recursive portion of the code ran out of items to recurse on.
- You would get a RuntimeError: maximum recursion depth exceeded.
- The function using recursion would return None.
Q59. What is the runtime complexity of searching for an item in a binary search tree?
- The runtime for searching in a binary search tree is O(1) because each node acts as a key, similar to a dictionary.
- The runtime for searching in a binary search tree is O(n!) because every node must be compared to every other node.
- The runtime for searching in a binary search tree is generally O(h), where h is the height of the tree.
- The runtime for searching in a binary search tree is O(n) because every node in the tree must be visited.
Q60. Why would you use mixin?
- You use a
mixinto force a function to accept an argument at runtime even if the argument wasn’t included in the function’s definition. - You use a
mixinto allow a decorator to accept keyword arguments. - You use a
mixinto make sure that a class’s attributes and methods don’t interfere with global variables and functions. - If you have many classes that all need to have the same functionality, you’d use a
mixinto define that functionality.
Q61. What is the runtime complexity of adding an item to a stack and removing an item from a stack?
- Add items to a stack in O(1) time and remove items from a stack on O(n) time.
- Add items to a stack in O(1) time and remove items from a stack in O(1) time.
- Add items to a stack in O(n) time and remove items from a stack on O(1) time.
- Add items to a stack in O(n) time and remove items from a stack on O(n) time.
Q62. Which statement accurately describes how items are added to and removed from a stack?
- a stacks adds items to one side and removes items from the other side.
- a stacks adds items to the top and removes items from the top.
- a stacks adds items to the top and removes items from anywhere in the stack.
- a stacks adds items to either end and removes items from either end.
Explanation Stack uses the last in first out approach
Q63. What is a base case in a recursive function?
- A base case is the condition that allows the algorithm to stop recursing. It is usually a problem that is small enough to solve directly.
- The base case is summary of the overall problem that needs to be solved.
- The base case is passed in as an argument to a function whose body makes use of recursion.
- The base case is similar to a base class, in that it can be inherited by another object.
Q64. Why is it considered good practice to open a file from within a Python script by using the with keyword?
- The
withkeyword lets you choose which application to open the file in. - The
withkeyword acts like aforloop, and lets you access each line in the file one by one. - There is no benefit to using the
withkeyword for opening a file in Python. - When you open a file using the
withkeyword in Python, Python will make sure the file gets closed, even if an exception or error is thrown.
Q65. Why would you use a virtual environment?
- Virtual environments create a “bubble” around your project so that any libraries or packages you install within it don’t affect your entire machine.
- Teams with remote employees use virtual environments so they can share code, do code reviews, and collaborate remotely.
- Virtual environments were common in Python 2 because they augmented missing features in the language. Virtual environments are not necessary in Python 3 due to advancements in the language.
- Virtual environments are tied to your GitHub or Bitbucket account, allowing you to access any of your repos virtually from any machine.
Q66. What is the correct way to run all the doctests in a given file from the command line?
python3 -m doctest <_filename_>python3 <_filename_>python3 <_filename_> rundoctestspython3 doctest
Q67. What is a lambda function ?
- any function that makes use of scientific or mathematical constants, often represented by Greek letters in academic writing
- a function that get executed when decorators are used
- any function whose definition is contained within five lines of code or fewer
- a small, anonymous function that can take any number of arguments but has only expression to evaluate
Explanation:
The lambda notation is basically an anonymous function that can take any number of arguments with only single expression (i.e, cannot be overloaded). It has been introducted in other programming languages, such as C++ and Java. The lambda notation allows programmers to “bypass” function declaration.
Q68. What is the primary difference between lists and tuples?
- You can access a specific element in a list by indexing to its position, but you cannot access a specific element in a tuple unless you iterate through the tuple
- Lists are mutable, meaning you can change the data that is inside them at any time. Tuples are immutable, meaning you cannot change the data that is inside them once you have created the tuple.
- Lists are immutable, meaning you cannot change the data that is inside them once you have created the list. Tuples are mutable, meaning you can change the data that is inside them at any time.
- Lists can hold several data types inside them at once, but tuples can only hold the same data type if multiple elements are present.
Q69. What does a generator return?
- None
- An iterable object
- A linked list data structure from a non-empty list
- All the keys of the given dictionary
Q70. What is the difference between class attributes and instance attributes?
- Instance attributes can be changed, but class attributes cannot be changed
- Class attributes are shared by all instances of the class. Instance attributes may be unique to just that instance
- There is no difference between class attributes and instance attributes
- Class attributes belong just to the class, not to instance of that class. Instance attributes are shared among all instances of a class
Q71. What is the correct syntax of creating an instance method?
- :
def get_next_card():
# method body goes here
- :
def get_next_card(self):
# method body goes here
- :
def self.get_next_card():
# method body goes here
- :
def self.get_next_card(self):
# method body goes here
Q72. What is the correct way to call a function?
get_max_num([57, 99, 31, 18])call.(get_max_num)def get_max_num([57, 99, 31, 18])call.get_max_num([57, 99, 31, 18])
Q73. How is comment created?
-- This is a comment# This is a comment/_ This is a comment _\// This is a comment
Q74. What is the correct syntax for replacing the string apple in the list with the string orange?
my_list = ['kiwi', 'apple', 'banana']
orange = my_list[1]my_list[1] = 'orange'my_list['orange'] = 1my_list[1] == orange
Q75. What will happen if you use a while loop and forget to include logic that eventually causes the while loop to stop?
- Nothing will happen; your computer knows when to stop running the code in the while loop.
- You will get a KeyError.
- Your code will get stuck in an infinite loop.
- You will get a WhileLoopError.
Q76. Describe the functionality of a queue?
- A queue adds items to either end and removes items from either end.
- A queue adds items to the top and removes items from the top.
- A queue adds items to the top, and removes items from anywhere in, a list.
- A queue adds items to the top and removes items from anywhere in the queue.
Q77. Which choice is the most syntactically correct example of the conditional branching?
- :
num_people = 5
if num_people > 10:
print("There is a lot of people in the pool.")
elif num_people > 4:
print("There are some people in the pool.")
else:
print("There is no one in the pool.")
- :
num_people = 5
if num_people > 10:
print("There is a lot of people in the pool.")
if num_people > 4:
print("There are some people in the pool.")
else:
print("There is no one in the pool.")
- :
num_people = 5
if num_people > 10;
print("There is a lot of people in the pool.")
elif num_people > 4;
print("There are some people in the pool.")
else;
print("There is no one in the pool.")
- :
if num_people > 10;
print("There is a lot of people in the pool.")
if num_people > 4;
print("There are some people in the pool.")
else;
print("There is no one in the pool.")
Q78. How does defaultdict work?
defaultdictwill automatically create a dictionary for you that has keys which are the integers 0-10.defaultdictforces a dictionary to only accept keys that are of the types specified when you created thedefaultdict(such as strings or integers).- If you try to read from a
defaultdictwith a nonexistent key, a new default key-value pair will be created for you instead of throwing aKeyError. defaultdictstores a copy of a dictionary in memory that you can default to if the original gets unintentionally modified.
Q79. What is the correct syntax for adding a key called variety to the fruit_info dictionary that has a value of Red Delicious?
fruit_info['variety'] == 'Red Delicious'fruit_info['variety'] = 'Red Delicious'red_delicious = fruit_info['variety']red_delicious == fruit_info['variety']
Q80. When would you use a while loop?
- when you want to minimize the use of strings in your code
- when you want to run code in one file while code in another file is also running
- when you want some code to continue running as long as some condition is true
- when you need to run two or more chunks of code at once within the same file
Simple Example
i = 1
while i<6:
print('Countdown:',i)
i = i + 1
Q81. What is the correct syntax for defining an __init__() method that sets instance-specific attributes upon creation of a new class instance?
- :
def __init__(self, attr1, attr2):
attr1 = attr1
attr2 = attr2
- :
def __init__(attr1, attr2):
attr1 = attr1
attr2 = attr2
- :
def __init__(self, attr1, attr2):
self.attr1 = attr1
self.attr2 = attr2
- :
def __init__(attr1, attr2):
self.attr1 = attr1
self.attr2 = attr2
Explanation: When instantiating a new object from a given class, the __init__() method will take both attr1 and attr2, and set its values to their corresponding object attribute, that’s why the need of using self.attr1 = attr1 instead of attr1 = attr1.
Q82. What would this recursive function print if it is called with no parameters?
def count_recursive(n=1):
if n > 3:
return
print(n)
count_recursive(n + 1)
- :
1
1
2
2
3
3
- :
3
2
1
- :
3
3
2
2
1
1
- :
1
2
3
Q83. In Python, when using sets, you use _ to calculate the intersection between two sets and _ to calculate the union.
Intersect;union|;&&;|&&;||
Q84. What will this code fragment return?
import numpy as np
np.ones([1,2,3,4,5])
- It returns a 5x5 matric; each row will have the values 1,2,3,4,5.
- It returns an array with the values 1,2,3,4,5
- It returns five different square matrices filled with ones. The first is 1x1, the second 2x2, and so on to 5x5
- It returns a 5-dimensional array of size 1x2x3x4x5 filled with 1s.
Q85. You encounter a FileNotFoundException while using just the filename in the open function. What might be the easiest solution?
- Make sure the file is on the system PATH
- Create a symbolic link to allow better access to the file
- Copy the file to the same directory as where the script is running from
- Add the path to the file to the PYTHONPATH environment variable
Q86. what will this command return?
{x for x in range(100) if x%3 == 0}
- a set of all the multiples of 3 less then 100
- a set of all the number from 0 to 100 multiplied by 3
- a list of all the multiples of 3 less then 100
- a set of all the multiples of 3 less then 100 excluding 0
Q87. What does the // operator in Python 3 allow you to do?
- Perform integer division
- Perform operations on exponents
- Find the remainder of a division operation
- Perform floating point division
Q88. What file is imported to use dates in python?
- datetime
- dateday
- daytime
- timedate
Q89. What is the correct syntax for defining a class called Game?
def Game(): passdef Game: passclass Game: passclass Game(): pass
Q90. What is the correct syntax for calling an instance method on a class named Game?
my_game = Game(self) self.my_game.roll_dice()my_game = Game() self.my_game.roll_dice()my_game = Game() my_game.roll_dice()my_game = Game(self) my_game.roll_dice(self)
Q91. What is the output of this code? (NumPy has been imported as np.)?
a = np.array([1,2,3,4])
print(a[[False, True, False, False]])
{0,2}[2]{2}[0,2,0,0]
Q92. Suppose you have a string variable defined as y=”stuff;thing;junk;”. What would be the output from this code?
z = y.split(';')
len(z)
- 17
- 4
- 0
- 3
Explanation:
y="stuff;thing;junk"
len(z) ==> 3
y="stuff;thing;junk;"
len(z) ==> 4
Q93. What is the output of this code?
num_list = [1,2,3,4,5]
num_list.remove(2)
print(num_list)
[1,2,4,5][1,3,4,5][3,4,5][1,2,3]
Explanation:
num_list = [1,2,3,4,5]
num_list.pop(3)
>>> [1,2,4,5]
num_list.remove(2)
>>> [1,3,4,5]
Q94. Which command will create a list from 10 down to 1? Example:
[10,9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1]
reversed(list(range(1,11)))list(reversed(range(1,10)))list(range(10,1,-1))list(reversed(range(1,11)))
Q95. Which fragment of code will print exactly the same output as this fragment?
import math
print(math.pow(2,10)) # prints 2 elevated to the 10th power
- :
print(2^10)
- :
print(2**10)
- :
y = [x*2 for x in range(1,10)]
print(y)
- :
y = 1
for i in range(1,10):
y = y * 2
print(y)
Q96. Elements surrounded by [] are _, {} are _, and () are _.
- sets only; lists or dictionaries; tuples
- lists; sets only; tuples
- tuples; sets or lists; dictionaries
- lists; dictionaries or sets; tuples
Q97. What is the output of this code? (NumPy has been imported as np.)
table = np.array([
[1,3],
[2,4]])
print(table.max(axis=1))
[2, 4][3, 4][4][1,2]
Q98. What will this code print?
number = 3
print (f"The number is {number}")
The number is 3the number is 3THE NUMBER IS 3- It throws a TypeError because the integer must be cast to a string.
Q99. Which syntax correctly creates a variable that is bound to a tuple?
my_tuple tup(2, 'apple', 3.5) %Dmy_tuple [2, 'apple', 3.5].tuple() %Dmy_tuple = (2, 'apple', 3.5)my_tuple = [2, 'apple', 3.5]
Q100. Which mode is not a valid way to access a file from within a Python script?
write('w')scan('s')append('a')read('r')
Q101. NumPy allows you to multiply two arrays without a for loop. This is an example of _.
- vectorization
- attributions
- accelaration
- functional programming
Q102. What built-in Python data type can be used as a hash table?
setlisttupledictionary
Q103. Which Python function allows you to execute Linux shell commands in Python?
sys.exc_info()os.system()os.getcwd()sys.executable
Q104. Suppose you have the following code snippet and want to extract a list with only the letters. Which fragment of code will _not_ achieve that goal?
my_dictionary = {
'A': 1,
'B': 2,
'C': 3,
'D': 4,
'E': 5
}
letters = []
for letter in my_dictionary.values():
letters.append(letter)
letters = my_dictionary.keys()letters = [letter for (letter, number) in my_dictionary.items()]letters4 = list(my_dictionary)
Explanation: The first one (the correct option) returns the list of the values (the numbers). The rest of the options return a list of the keys.
Q105. When an array is large, NumPy will not print the entire array when given the built-in print function. What function can you use within NumPy to force it to print the entire array?
set_printparamsset_printoptionsset_fullprintsetp_printwhole
Q106. When would you use a try/except block in code?
- You use
try/exceptblocks when you want to run some code, but need a way to execute different code if an exception is raised. - You use
try/exceptblocks inside of unit tests so that the unit testes will always pass. - You use
try/exceptblocks so that you can demonstrate to your code reviewers that you tried a new approach, but if the new approach is not what they were looking for, they can leave comments under theexceptkeyword. - You use
try/exceptblocks so that none of your functions or methods returnNone.
Q107. In Python, how can the compiler identify the inner block of a for loop?
because of the level of indentation after the for loopbecause of the end keyword at the end of the for loopbecause of the block is surrounded by brackets ({})because of the blank space at the end of the body of the for loop
Q108. What Python mechanism is best suited for telling a user they are using a deprecated function
- sys.stdout
- traceback
- warnings
- exceptions
Q109. What will be the value of x after running this code?
x = {1,2,3,4,5}
x.add(5)
x.add(6)
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 5, 6}{5, 6, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}{6, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5}{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
Explanation: The .add() method adds the element to the set only if it doesn’t exist.
Q110. How would you access and store all of the keys in this dictionary at once?
fruit_info = {
'fruit': 'apple',
'count': 2,
'price': 3.5
}
my_keys = fruit_info.to_keys()my_keys = fruit_info.all_keys()my_keys = fruit_info.keysmy_keys = fruit_info.keys()
Q111. What is wrong with this function definition?
def be_friendly(greet = "How are you!", name):
pass
nameis a reserved word.- Underscores are not allowed in function names.
- A non-default argument follows a default argument.
- There is nothing wrong with this function definition.
Q112. Given that NumPy is imported as np, which choice will return True?
- :
a = np.zeros([3,4])
b = a.copy()
np.array_equal(a,b)
- :
a = np.empty([3,4])
b = np.empty([3,4])
np.array_equal(a,b)
- :
a = np.zeros([3,4])
b = np.zeros([4,3])
np.array_equal(a,b)
- :
a = np.array([1, np.nan])
np.array_equal(a,a)
Q113. How do you add a comment to existing Python script?
// This is a comment# This is a comment-- This is a comment/* This is a comment *\
Q114. In this code fragment, what will the values of c and d be equivalent to?
import numpy as np
a = np.array([1,2,3])
b = np.array([4,5,6])
c = a*b
d = np.dot(a,b)
- A
c = [ a[1] * b[1], a[2] * b[2], a[3] * b[3] ]
d = sum(c)
- B
c = a[0] * b[0], a[1] * b[1], a[2] * b[2]
d = [ a[0] * b[0], a[1] * b[1], a[2] * b[2] ]
- C
c = [ a[0] * b[0], a[1] * b[1], a[2] * b[2] ]
d = sum(a) + sum(b)
- D
c = [ a[0] * b[0], a[1] * b[1], a[2] * b[2] ]
d = sum(c)
Q115. What two functions within the NumPy library could you use to solve a system of linear equations?
linalg.eig() and .matmul()linalg.inv() and .dot()linalg.det() and .dot()linalg.inv() and .eye()
Q116. What is the correct syntax for creating a variable that is bound to a list?
my_list = (2, 'apple', 3.5)my_list = [2, 'apple', 3.5]my_list = [2, 'apple', 3.5].to_list()my_list = to_list(2, 'apple', 3.5)
Q117. This code provides the _ of the list of numbers.
num_list = [21, 13, 19, 3, 11, 5, 18]
num_list.sort()
num_list[len(num_list) // 2]
- mode
- average
- mean
- median
Explanation: The median is the value separating the higher half from the lower half of a data sample. Here it is 13.
Q118. What are the two main data structures in the Pandas library?
- Arrays and DataFrames
- Series and Matrixes
- Matrixes and DataFrames
- Series and DataFrames
Q119. Suppose you have a variable named vector of type np.array with 10,000 elements. How can you turn vector into a variable named matrix with dimensions 100x100?
matrix = (vector.shape = (100,100))matrix = vector.to_matrix(100,100)matrix = matrix(vector,100,100)matrix = vector.reshape(100, 100)
Q120. Which choice is an immutable data type?
- dictionnary
- list
- set
- string
Q121. What is the output of this code?
def myFunction(country = "France"):
print("Hello, I am from", country)
myFunction("Spain")
myFunction("")
myFunction()
- :
Hello, I am from Spain
Hello, I am from
Hello, I am from
- :
Hello, I am from France
Hello, I am from France
Hello, I am from France
- :
Hello, I am from Spain
Hello, I am from
Hello, I am from France
- :
Hello, I am from Spain
Hello, I am from France
Hello, I am from France
Q122. Choose the option below for which instance of the class cannot be created
- Anonymous Class
- Parent Class
- Nested Class
- Abstract Class
Q123. Using Pandas, we load a data set from Kaggle, as structured in the image below. Which command will return the total number of survivors?
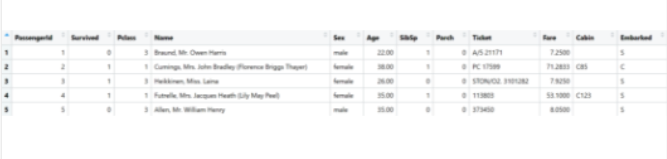
sum(titanic['Survived'])[x for x in titanic['Survived'] if x == 1]len(titanic["Survived"])sum(titanic['Survived']==0)
Explanation: The titanic['Survived'] returns a pandas.Series object, which contains the Survived column of the DataFrame.
Adding the values of this column (i.e. sum(titanic['Survived'])) returns the total number of survivors since a survivor is represented by a 1 and a loss by 0.
Q124. How would you create a list of tuples matching these lists of characters and actors?
characters = ["Iron Man", "Spider Man", "Captain America"]
actors = ["Downey", "Holland", "Evans"]
# example output : [("IronMan", "Downey"), ("Spider Man", "Holland"), ("Captain America", "Evans")]
[(x,y)] for x in characters for y in actors]zip(characters, actors)- [ ]
d = {}
for x in range(1, len(characters)):
d[x] = actors[x]
{x:y for x in characters for y in actors}
Q125. What will this statement return?
{x : x*x for x in range(1,100)}
- a dictionary with x as a key, and x squared as its value; from 1 to 100
- a dictionary with x as a key, and x squared as its value; from 1 to 99
- a set of tuples, consisting of (x, x squared); from 1 to 99
- a list with all numbers squared from 1 to 99
Q126. Jaccard Similarity is a formula that tells you how similar two sets are. It is defined as the cardinality of the intersection divided by the cardinality of the union. Which choice is an accurate implementation in Python?
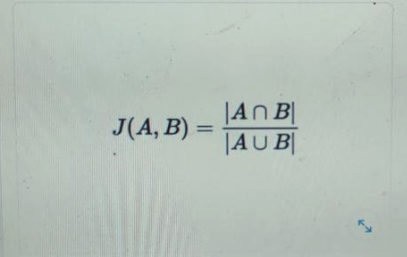
def jaccard(a, b): return len (a | b) / len (a & b)def jaccard(a, b): return len (a & b) / len (a | b)def jaccard(a, b): return len (a && b) / len (a || b)def jaccard(a, b): return a.intersection(b) / a.union(b)
Q127. Which choice is not a native numerical type in Python?
- Long
- Int
- Float
- Double
Q128. What will be the output of this code?
[1,2,3] * 3
[3,2,3][1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3]- You will get a type error.
[3,6,9]
Q129. Given a list defined as numbers = [1,2,3,4], what is the value of numbers[-2]?
- 1
- 3
- 2
- An IndexError exception is thrown.
Q130. Which statement about strings in Python is true?
- Strings can be enclosed by double quotes (“) or single quotes (‘).
- Strings can only be enclosed in single quotes (‘).
- Single character strings must be enclosed in single quotes (‘), and the rest must be enclosed in double quotes (“).
- Strings can only be enclosed in double quotes (“).
Q131. What is the correct syntax for defining an init() method that takes no parameters?
- definit(self): pass
- classinit(self): pass
- classinit(): pass
- definit(): pass
() -empty parameter self -refers to all instances within a class init -a reserved method, aka a constructor init() -always executed when the class is being initiated
Q132. Suppose you need to use the sin function from the math library. What is the correct syntax for importing only that function?
using math.sinimport math.sinfrom math import sinimport sin from math
Q133. What do you get if you apply numpy.sum() to a list that contains only Boolean values?
0the count of all True valuesa type errorNone
Q134. What will this code print?
print ("foo" if (256).bit_length() > 8 else "bar")
- True
- foo
- You will get an error message because constant integer values are not classes.
- bar
Q135. If you do not explicitly return a value from a function, what happens?
- If the return keyword is absent, the function will return True.
- The function will enter an infinite loop because it will not know when to stop executing its code.
- The function will return a RuntimeError if you do not return a value.
- If the return keyword is absent the function will return None.
Q136. it is often the case that the pandas library is used for _ data and NumPy for _ data.
- string; numerical
- unstructured; structured
- numerical; tabular
- tabular; numerical
Q137. What do you need to do to install additional packages into Python?
- Use a C compiler like gcc or clang.
- Use a package manager like pip or conda.
- Use an IDE like Notepad++ or Idle.
- Use a package manager like NPM or NuGet.
Q138. The image below was created using Matplotlib. It is a distribution plot of a list of integers filled with numbers using the function _ and plotted with _.
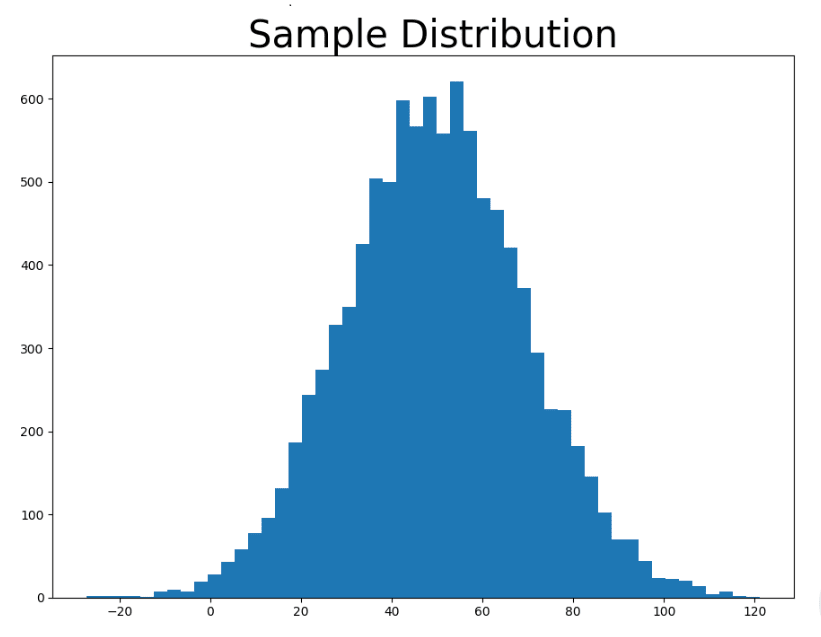
random.uniform(0,50);plt.histrandom.gauss(50,20);plt.histrandom();plt.scatterrandom.triangular(0,50);plt.bar
Q139. In this code fragment, what will be the values of a and b ?
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(100)
b = a[50:60:2]
- a: all integers from 0 to 99 (inclusive) b: all even integers from 50 to 58 (inclusive)
- a: all integers from 0 to 100 (inclusive) b: all even integers from 50 to 60 (inclusive)
- a: all integers from 0 to 99 (inclusive) b: all even integers from 50 to 60 (inclusive)
- a: all integers from 0 to 99 (inclusive) b: all odd integers from 49 to 59 (inclusive)
Q140. When using NumPy in Python, how do you check the dimensionality (number and length of dimensions) of an object called my_object?
my_object.get_shape()my_object.shapemy_object.dim()len(my_object)
Q141. Assume you have a non-empty list named mylist and you want to search for a specific value. The minimum number of comparison will be __ and the maximum number of comparison will be _?
len(mylist); len(mylist)1; len(mylist)2; len(mylist)0; len(mylist)
Explanation: Can use a break statement and the value being searched can be the first element of the list, given that it is non-empty.
Q142. If a function does not have a return statement, what does it really return?
- 0
- True
- None
- False
Q143. What is a common use of python’s sys library?
- to capture command-line arguments given at a file’s runtime
- to take a snapshot of all the packages and libraries in your virtual environment
- to connect various systems, such as connecting a web front end, an API service, a database, and a mobile app
- to scan the health of your Python ecosystem while inside a virtual environment
Q144. Suppose you want to double-check if two matrices can be multipled using NumPy for debugging purposes. How would you complete this code fragment by filling in the blanks with the appropiate variables?
import numpy as np
def can_matrices_be_multiplied (matrix1, matrix2):
rowsMat1, columnsMat1 = matrix1.shape
rowsMat2, columnsMat2 = matrix2.shape
if _____ == ______ :
print('The matrices can be multipled!')
return True
else:
return False
- columnsMat1; rowsMat1;
- columnsMat1; rowsMat2;
- columnsMat1; columnsMat2;
- columnsMat2; rowsMat1;
Q145. What is the output of this comprehension?
[(x, x+1) for x in range(1,5)]
- [(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4), (4, 5), (5, 6)]
- [1,2,3,4,5]
- [(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4)]
- [(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4), (4, 5)]
Q146. In Python, a class method must have __ as a function decorator, and the first parameter of the method will be a reference to __.
- @classmethod; the class
- inline; the class
- static; self
- @static; self
Q147. Which snippet of code will print My name is Joffrey, son of Robert?
- :
class Father():
name = 'Robert'
class Person(Father):
def __init__(self, name):
self.fathername = super.name
self.name = name
def introduce(self):
print("My name is", self.name, "son of", self.fathername)
king = Person("Joffrey")
king.introduce()
- :
class Father():
name = 'Robert'
class Person(Father):
def __init__(self, name):
self.fathername = self.name
self.name = name
def introduce(self):
print("My name is", self.name, "son of", self.fathername)
king = Person("Joffrey")
king.introduce()
- :
class Father():
name = 'Robert'
class Person(Father):
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
def introduce(self):
print("My name is", self.name, "son of", super.name)
king = Person("Joffrey")
king.introduce()
- :
class Father():
name = 'Robert'
class Person(Father):
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
def introduce(self):
print("My name is", self.name, "son of", base.name)
king = Person("Joffrey")
king.introduce()
Explanation: In the first, super does not have .name (should be self.name), The third drops Robert, and base is not defined in the 4th.
Q148.
animals = {
'a': ['ant', 'antelope', 'armadillo'],
'b': ['beetle', 'bear', 'bat'],
'c': ['cat', 'cougar', 'camel']
}
animals = defaultdict(list, animals)
print(animals['b'])
print(animals['d'])
- A
['beetle', 'bear', 'bat']
[]
- B
['beetle', 'bear', 'bat']
# an exception will be thrown
- C
['beetle', 'bear', 'bat']
None
- D
['bat', 'bear', 'beetle']
[]
Explanation: Dictionaries usually result in an exception when using the square bracket syntax. Defaultdict here returns a default value dedicated by the first parameter so instead of throwing an exception, they return the default. Note that this needs to be imported as follows: from collections import defaultdict
Q149. What will this line of code return? (Assume n is already defined as any positive integer value.)
[x*2 for x in range(1,n)]
- a list with all the even numbers less than 2*n
- a dictionary with all the even numbers less than 2*n
- a list with all the odd numbers less than 2*n
- a list with all the even numbers less than or equal to 2*n
Q150. What does this code print in the console?
x = 18
if x > 10:
if x > 15:
print('A')
else:
print('B')
else:
print('C')
- C
- A B
- B
- A
Q151. Suppose you have a variable named vector of type np.array with 10.000 elements. How can you turn vector into a variable named matrix with dimensions 100x100?
- matrix = matrix(vector,100,100)
- matrix = vector.to_matrix(100,100)
- matrix = (vector.shape = (100,100))
- matrix = vector.reshape(100,100) Exa
Q152. What is the maximum length of a Python identifier?
- 32
- 16
- 128
- No fixed length is specified
Q153. What will the value of the i variable be when the following loop finishes its execution?
for i in range(5): pass
- 5
- the variable becomes unavailable
- 6
- 4
Q154. f-strings are also called:
- Formatted string expressions
- Functional strings
- Modulo formatted strings
- Formatted string literals
Q155. How many CPUs (or cores) will the Python threading library take advantage of simultaneously?
- One
- All of the available CPUs
- Two
- Three
Explanation: Python threading is restricted to a single CPU at one time. The multiprocessing library will allow you to run code on different processors.
Q156 What will be the value of y in this code?
x = 5
y = 1 + (20 if x < 5 else 30)
- False
- 21
- 2
- 31
Explanation: If x < 5 ==> y = 1 + 20 Else y = 1 + 30
Q157.The process of pickling in Python includes?
- conversion of a Python object hierarchy into byte stream
- conversion of a datatable into a list
- conversion of a byte stream into Python object hierarchy
- conversion of a list into a datatable
Explanation:Pickling is the process of sterilizing a Python object, that is, conversion of a byte stream into Python object hierarchy. The reverse of this process is known as unpickling.
Q158. What is the output of the following program ?
print("codescracker".endswith("er"))
- True
- 1
- 2
- False
Q159. Is list mutable in python ?
- True
- False
Q160. What is the output of the following program ?
print(“programming”.center())
- cr
- programming
- Error says TypeError: center expected at least 1 argument, got 0
- None of the Above
Q161. Who created the Python programming language?
- Tim Berners-Lee
- Ada Lovelace
- Guido van Rossum
- Alan Turing
Q162. Which collection is ordered, changeable, and allows duplicate members?
- SET
- TUPLE
- DICTIONARY
- LIST
Q163. What will be printed in the console if you run this code?
x = 1j
print(x**2 == -1)
- a run-time error telling you that the variable
jhas not been initialized - True
- 1j
- False
Explanation: The letter j acts as the imaginary unit in Python, therefore x**2 means j**2 which is equal to -1. The statement x**2 == -1 is evaluated as True.
Q164. What will be printed in the console if you run this code?
print(0xA + 0xB + 0xC)
- 33
- 63
- 0xA + 0xB + 0xC
- None
Explanation: A, B and C are hexadecimal integers with values 10, 11 and 12 respectively, so the sum of A, B and C is 33.
Q165. What will this code output to the screen?
for i in range(5):
print(i)
else:
print("Done!")
- 1 2 3 4 5 Done!
- 0 1 2 3 4 5 Done!
- 0 1 2 3 4 Done!
- You will get a syntax error.
Q166. Which comparison of lists and tuples in Python is correct?
- Use lists instead of tuples when you have a collection of related but dissimilar objects.
- Use tuples instead of lists when you have a common collection of similar objects.
- Use tuples instead of lists for functions that need to return multiple values.
- Use lists instead of tuples when the position of elements is important.
Q167. Consider the following code snippet that uses decorators to calculate the execution time of execution_fn function:
import functools
import time
def timer(MISSING_ARG_1):
@functools.wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
start_time = time.perf_counter()
rval = func(*args, **kwargs)
end_time = time.perf_counter()
duration = end_time - start_time
print(f"Executed in {duration:.4f} seconds")
return MISSING_ARG_2
return MISSING_ARG_3
@timer
def execution_fn():
for i in range(3):
time.sleep(1)
execution_fn()
Which of the following choices are the missing arguments?
- :
MISSING_ARG_1 = wrapper
MISSING_ARG_2 = rval
MISSING_ARG_3 = func
- :
MISSING_ARG_1 = func
MISSING_ARG_2 = rval
MISSING_ARG_3 = wrapper
- :
MISSING_ARG_1 is empty
MISSING_ARG_2 = rval
MISSING_ARG_3 = wrapper
- :
MISSING_ARG_1 is empty
MISSING_ARG_2 = rval
MISSING_ARG_3 = func
Q168. Which of the following statements defines a new object type named “Dog” in Python?
- class Dog:
- Dog class:
- Dog:
- class Dog
Q169. To use pipelines in scikit-learn, import from the scikit-learn._ submodule.
- preprocessing
- pipeline
- filters
- pipe_filter
Q170. You should pass in a value of _ for the axis argument to the Pandas apply method to apply the function to each row.
- row
- col
- 1
- 0
Q171. Data points in pyplot are called
- pointers
- points
- markers
- none of these
Q172. What does this code print?
a = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]])
c = a[(a > 3) & (a < 11)]
print(c)
[[3, 4], [5, 6]][False, False, False, True, True, True][[0,0], [3, 4], [5, 6]][4 5 6]